Imagenes biomédicas
Plantar Fascia Rupture Following Soccer Injury: A Case of Conservative Treatment and Recovery
Rotura de la fascia plantar tras una lesión de fútbol: un caso de tratamiento conservador y recuperación
Ruptura da fáscia plantar após lesão no futebol: um caso de tratamento conservador e recuperação
1Universidade de Ribeirão Preto. Campus Guarujá, Guarujá (SP), Brasil. Correo eletrónico: gui_fully@hotmail.com, lgdebonis@gmail.com.
2Universidade de Ribeirão Preto. Campus Guarujá, Guarujá (SP), Brasil. Diagnósticos da América S.A. - DASA, São Paulo (SP), Brasil. Correo eletrónico: marcioluisduarte@gmail.com.
Abstract
The plantar fascia is divided into three bands, each crucial for foot support. Differentiating between plantar fasciitis and plantar fascia rupture is essential due to their distinct treatment approaches. MRI is the best test to diagnose the disease. We present a case of 42-year-old man experienced severe pain in his left foot one day after hearing a “pop” while playing soccer.
Keywords: Fasciitis, Plantar; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Ankle
Resumen
La fascia plantar se divide en tres bandas, cada una de ellas crucial para el apoyo del pie. Diferenciar entre fascitis plantar y rotura de fascia plantar es esencial debido a sus distintos enfoques de tratamiento. La resonancia magnética es la mejor prueba para diagnosticar la enfermedad. Presentamos el caso de un hombre de 42 años que experimentó un dolor intenso en el pie izquierdo un día después de escuchar un "pop" mientras jugaba al fútbol.
Keywords: Fascitis Plantar; Imagen por Resonancia Magnética; Tobillo
Resumo
A fáscia plantar é dividida em três bandas, cada uma crucial para o suporte do pé. Diferenciar entre fascite plantar e ruptura da fáscia plantar é essencial devido às suas distintas abordagens de tratamento. A ressonância magnética é o melhor teste para diagnosticar a doença. Apresentamos o caso de um homem de 42 anos que sentiu dor intensa no pé esquerdo um dia após ouvir um "estalo" enquanto jogava futebol.
Palavras-chave: Fasciíte Plantar; Imageamento por Ressonância Magnética; Tornozelo
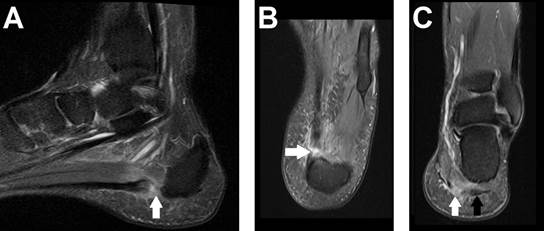
A 42-year-old man developed severe left foot pain after hearing a “pop” while playing soccer. He had experienced plantar pain for three months, aggravated by wearing boots at work. Examination revealed plantar tenderness without significant bruising or swelling, and he walked with a limp. MRI showed plantar fasciitis in the lateral band and a complete rupture of the central band at its insertion (Figure 1). He was treated with analgesics and physical therapy, achieving full recovery in three months.
The plantar fascia consists of three bands.1 Rupture is much less common than plantar fasciitis, occurring in approximately 12% of cases2 Acute tears may be spontaneous or result from chronic degeneration, often in athletes, and typically cause pain, bruising, swelling, and tenderness. (1,3 Patients frequently report a “pop” and an inability to perform a single-leg heel raise. (2 Sonography shows partial or complete fascial disruption with hypoechoic hemorrhagic tissue, while MRI, the gold standard, reveals high-signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences. (4
Risk factors include obesity, flat feet, bone spurs, high-impact activities, and prior steroid injections. (3 Treatment is primarily conservative, involving immobilization, limited weight-bearing, NSAIDs, and physical therapy. (5 According to the systematic review of Debus et al, no standardized guidelines exist, and management varies. (2 Surgery is reserved for refractory cases. (6
References:
1. Costa D, Cruz P, Brito R, Cantista P, Rodrigues-Gomes S. Acute Rupture of the Plantar Fascia in a Soccer Player. Cureus. 2023 May 4;15(5):e38527. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38527.
[ Links ]
2. Debus F, Eschbach D, Ruchholtz S, Peterlein CD. Rupture of plantar fascia: Current standard of therapy: A systematic literature review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020 Jun;26(4):358-362. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2019.05.006.
[ Links ]
3. Lee HS, Choi YR, Kim SW, Lee JY, Seo JH, Jeong JJ. Risk factors affecting chronic rupture of the plantar fascia. Foot Ankle Int. 2014 Mar;35(3):258-63. doi: 10.1177/1071100713514564.
[ Links ]
4. Elias DA, Carne A, Bethapudi S, Engebretsen L, Budgett R, O’Connor P.(2013). Imaging of plantar fascia and Achilles injuries undertaken at the London 2012 Olympics. Skeletal Radiology, 42(12), 1645–1655. doi:10.1007/s00256-013-1689-1.
[ Links ]
5. Coppola M, Sgadari A, Marasco D, Danti C, Vitale G, Smeraglia F, Balato G, Bernasconi A. Treatment Approaches for Plantar Fasciopathy in Elite Athletes: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022 Nov 28;10(11):23259671221136496. doi: 10.1177/23259671221136496.
[ Links ]
6. Draghi F, Gitto S, Bortolotto C, Draghi AG, Ori Belometti G. Imaging of plantar fascia disorders: findings on plain radiography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Insights Imaging. 2017 Feb;8(1):69-78. doi: 10.1007/s13244-016-0533-2
[ Links ]